IWLA 0.6
Almost 3 years since the last news about IWLA. It does not really reflect the continuous development & maintenance of this wonderful tool. But don't worry, version 0.6 is now out ! The main change is the complete move from Python 2 to Python 3, but we may also mention :
- Users requests are no more saved (except if keep_requests is set) which allow to save a LOT of space
- A favicon is available
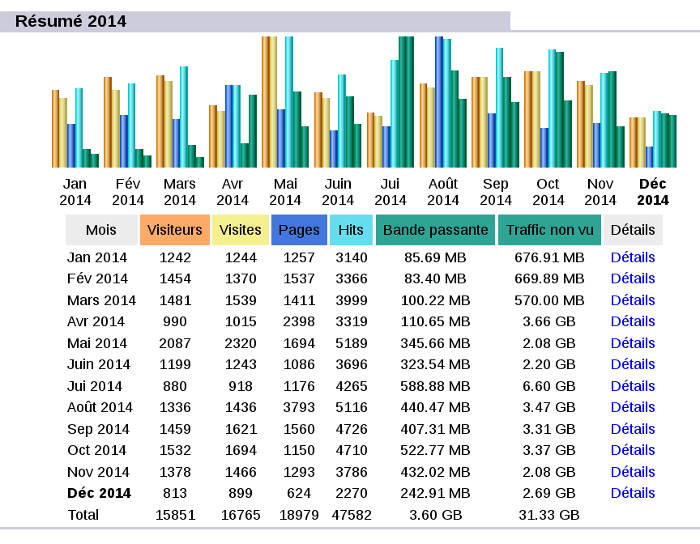
- Fresh synchronization with AWSTATS data
- Users need to do at least one hit per viewed page to not be marked as a robot
- Feed detector has been enhanced
- Track users plugin has been replaced by filter users which allows to define complex filters
- Users can be enlighted in all visits page
- IP can be anonymized (for public statistics)
The full ChangeLog is available here
While working on it, I realized how we can easily extend it. It's a real pleasure comparing to so big one PERL file code of AWSTATS, plus having it modular allows to implement our own rules which makes statistics really more precise. The only issue compared to AWSTATS is that IWLA is only focused on web statistics, but it has been design for it, not for everything related to log parsing !
New : A demo instance (for indefero.soutade.fr) is available here
I also decided to give up the old style branching model with master and dev. Using git and its lightweight branches, it's better to have a model with tags for stable releases and features branch for development. Code is not often updated and it makes no sense to have a master branch updated every 3 years with only one merge commit while dev is living.
I recently had look on concurrence, especially with Matomo and I was really afraid to see how users are tracked ! Everything is managed from pages viewed to cursor moves, user system information retrieval, time spent... All of this generate extra traffic and requires to execute Javascript code to obtain a lot of information about users's environment. But it's not the worst tool as it doesn't use commercial tracking (like Google Analytics) and keep data on webmaster's server and it's certified RGPD compliant. Commercial trackers are really a nightmare for consumer's privacy. Using it, webmaster can obtain really good statistics, but everything is stored on (abroad) commercial servers to create your profile ! Your profile is then sold or used to display you personalized advertising. Unfortunately, almost all websites are using them. In opposite, IWLA requires no cookies, no Javascript, no awful banner. It only parse and analyze log requests from webserver and generate a static HTML report which is the only right way to do !